By: Dr. Elizabeth Eggert
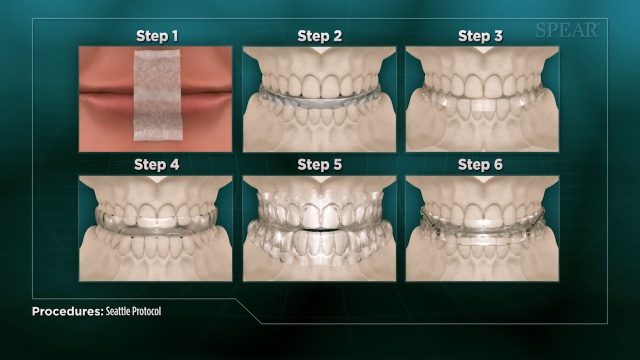
When a patient with symptoms of airway issues first comes into our office, we often recommend the Seattle Protocol. This six-step method helps us identify where the issue lies by pinpointing which jaw positioning alleviates our patient’s symptoms. This allows us to create a custom night appliance for our patient that opens up their airway and curbs any inflammation or damage to the teeth, jaws or soft tissue. It also helps ward off serious systemic issues like high blood pressure, stroke or heart attack.
Before you embark on the Seattle Protocol, we may suggest an at-home sleep quality screening device or a sleep study so we solidify our starting point.
Seattle Protocol Step 1: Nose Breathing and Mouth Taping
The first step in the Seattle Protocol is to gently train your body to breathe through your nose, not your mouth. Breathing through your mouth during sleep can lead to snoring and a dry mouth. The Seattle Protocol encourages nose breathing by adding a strip of paper tape vertically across the center of your lips. The light adhesive of the tape keeps your lips together but is easy and painless to remove.
Step 2: Temporary Splint for Lower Jaw and Mouth Taping
Once you’ve adjusted to the mouth taping, the second step of the protocol adds a temporary splint for your lower jaw while you sleep. Adding this splint increases the vertical dimension of your jaw and allows more airway space.
Step 3: Temporary Splint for Lower Jaw with Lower Jaw Pulled Forward and Mouth Taping
If adding the lower splint only isn’t giving you the restful sleep you deserve, we move onto the next stage of the protocol. In this step, we add an element that pulls your lower jaw forward. This realigns your jaw and increases your airway space not only vertically, but horizontally as well. This also can give your tongue more of the space it requires.
Step 4: Temporary Splint for Lower and Upper Jaw with Mouth Taping
With all steps of the Seattle Protocol, if you aren’t getting relief from the previous step, we move on. In this step, we remove the forward jaw posturing component and add a splint for your upper jaw. You then go to sleep with splints on your upper and lower teeth and your jaw is free to move. This stage allows for additional vertical height, opening up your airway, but without restricting the jaw muscles into any one strict position.
Step 5: Temporary Splint for Lower and Upper Jaw with Lower Jaw Pulled Forward and Mouth Taping
If you need to continue in the protocol, step five again adds a horizontal component by linking the upper and lower splints together and moving the lower jaw forward. The intent, as always, is to continue to open your airway more and more.
Step 6: Temporary Splint for Lower and Upper Jaw with Lower Jaw Progressively Pulled Forward and Mouth Taping
If you still aren’t getting that good night’s sleep, we move to the final stage of the Seattle Protocol. In this stage, we keep moving your lower jaw forward, incrementally, until you feel well-rested.
In summary, after the initial two weeks of nasal breathing therapy and sleeping for 2-3 nights with each temporary night guard, once you experience relief of symptoms, we stop the protocol. This helps us identify which splint appliance/positioning alleviates the airway obstruction and allows us to fabricate your custom night appliance.
The further you progress through the steps in the protocol, the more severe your obstruction. If you progress into steps 4, 5 or 6, we may discuss the possibility of oral surgery to help you achieve optimal results.
If you’re concerned that you or your loved ones are dealing with sleep-disordered breathing, schedule an appointment with Dr. Elizabeth or Dr. Jeff by calling our office at 651.482.8412. Both Dr. Elizabeth and Dr. Jeff have the knowledge and experience to walk you through the Seattle Protocol and the best next steps.
Your healthy future starts today.